A Guide to LLM Evals
Deep Dives
Explore related topics with these Wikipedia articles, rewritten for enjoyable reading:
-
Goodhart's law
17 min read
Directly relevant to LLM evaluation challenges - when models are optimized for benchmark metrics, those metrics cease to be good measures of actual capability. The article discusses how benchmark optimization can diverge from genuine performance.
-
Inter-rater reliability
11 min read
The article discusses human evaluation and preference ranking but doesn't explain the statistical foundations. Understanding how to measure agreement between human raters is essential for valid human evaluations of LLMs.
-
BLEU
12 min read
The article mentions BLEU as a text generation metric with 'known limitations' but doesn't explain what it is or why it's problematic. Understanding this foundational NLP metric and its history provides valuable context for modern LLM evaluation.
The Developer's Guide to MCP Auth (Sponsored)
Securely authorizing access to an MCP server is complex. You need PKCE, scopes, consent flows, and a way to revoke access when needed.
Learn from WorkOS how to implement OAuth 2.1 in a production-ready setup, with clear steps and examples.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have moved from research labs into production applications at a remarkable pace. Developers are using them for everything from customer support chatbots to code generation tools to content creation systems. However, this rapid adoption brings an important question: how do we know if our LLM is actually working well?
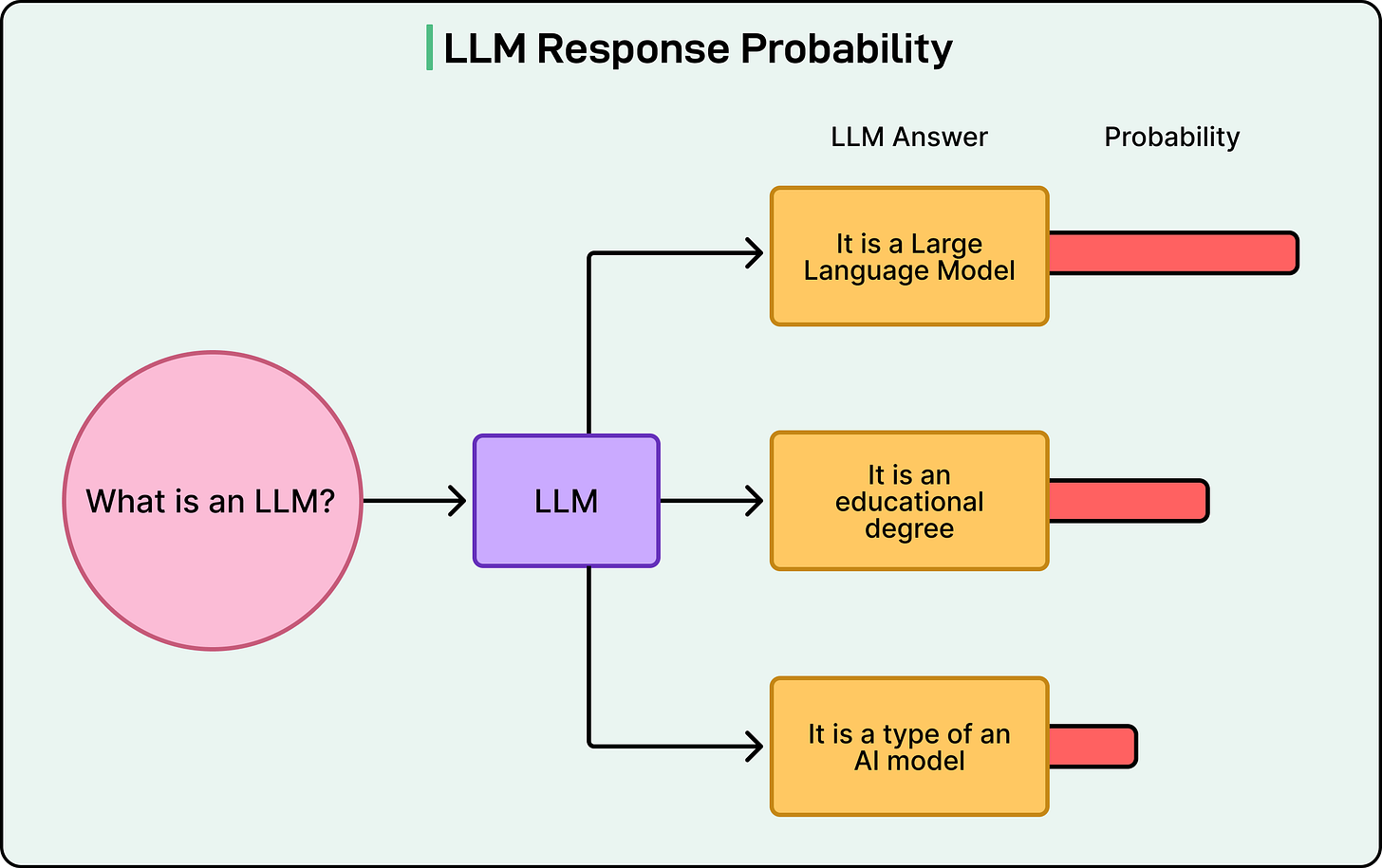
Unlike traditional software, where we can write unit tests that check for exact outputs, LLMs are probabilistic systems. Ask the same question twice, and the model might give different answers, both of which could be perfectly valid. This uncertainty makes evaluation challenging but absolutely necessary.
This is where “evals” come in. Short for evaluations, evals are the systematic methods we use to measure how well our LLM performs. Without proper evaluation, we’re essentially flying blind, unable to know whether our latest prompt change made things better or worse, whether our model is ready for production, or whether it’s handling edge cases correctly.
In this article, we’ll explore why LLM evaluation is challenging, the different types of evaluations available, key concepts to understand, and practical guidance on setting up an evaluation process.
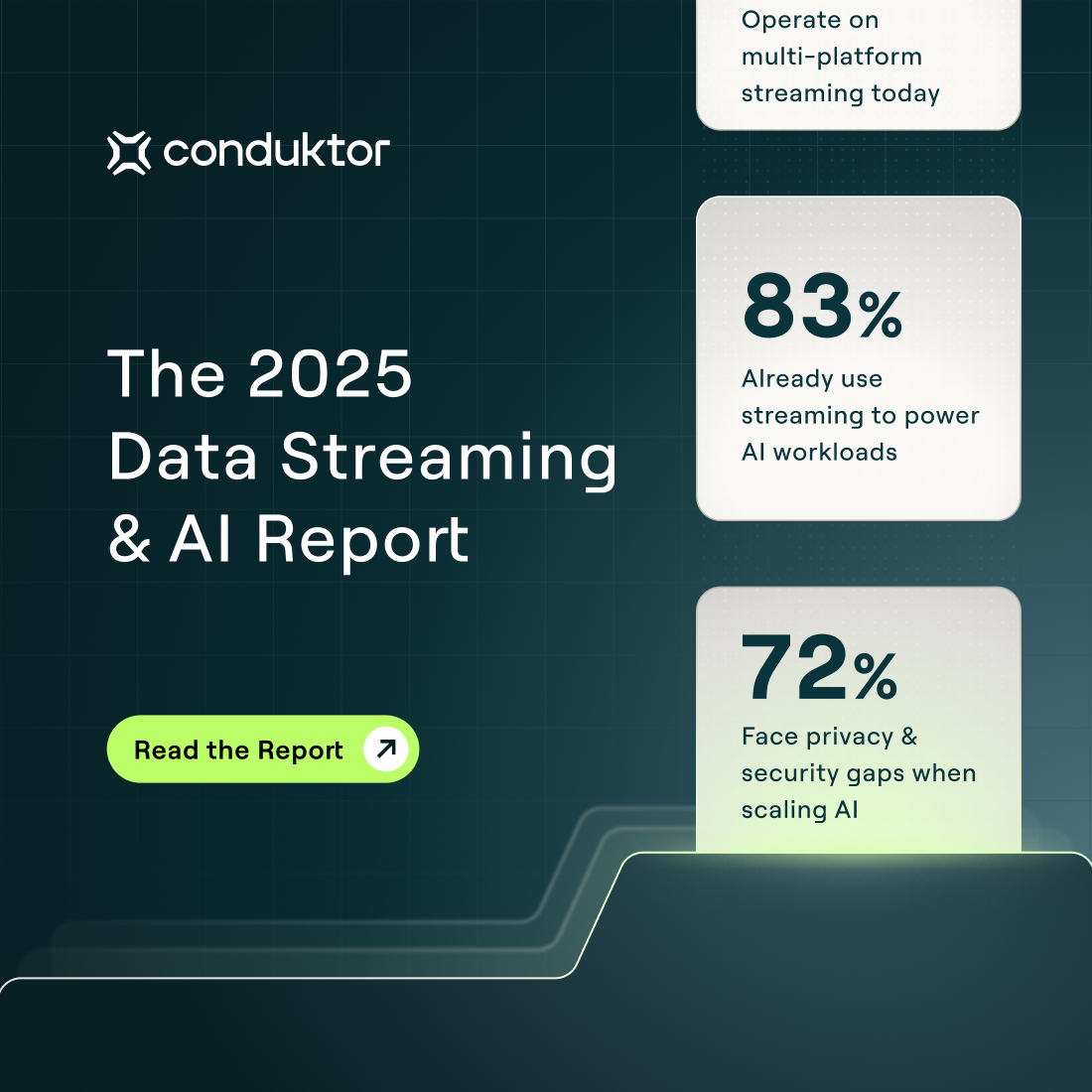
The 2025 Data Streaming & AI Report (Sponsored)
AI is only as powerful as the data behind it — but most teams aren’t ready.
We surveyed 200 senior IT and data leaders to uncover how enterprises are really using streaming to power AI, and where the biggest gaps still exist.
Discover the biggest challenges in real-time data infrastructure, the top obstacles slowing down AI adoption, and what high-performing teams are doing differently in 2025.
Download the full report to see where your organisation stands.
Why LLM Evaluation Is Challenging
If we’re used to testing traditional software, LLM evaluation will feel different in fundamental ways. In conventional programming, we write a function that takes an input and produces a deterministic output. Testing is straightforward. Given input X, we expect output Y. If we get Y, the test passes. If not, it fails.
LLMs break this model in several ways.
First, there’s the subjective nature of language itself. What makes a response “good”? One response might be concise while another is
This excerpt is provided for preview purposes. Full article content is available on the original publication.