BioByte 136: Scaling Laws for pLMs, DeepSomatic and CASTLE for Oncological Variant Calling, Ballistic Microscopy for Cellular Imaging, Neural Circuitry for Encoding of Inferred Contours
Welcome to Decoding Bio’s BioByte: each week our writing collective highlight notable news—from the latest scientific papers to the latest funding rounds—and everything in between. All in one place.
What we read
Blogs
Do Scaling Laws Hold for Protein Language Models? [Align Bio, October 2025]
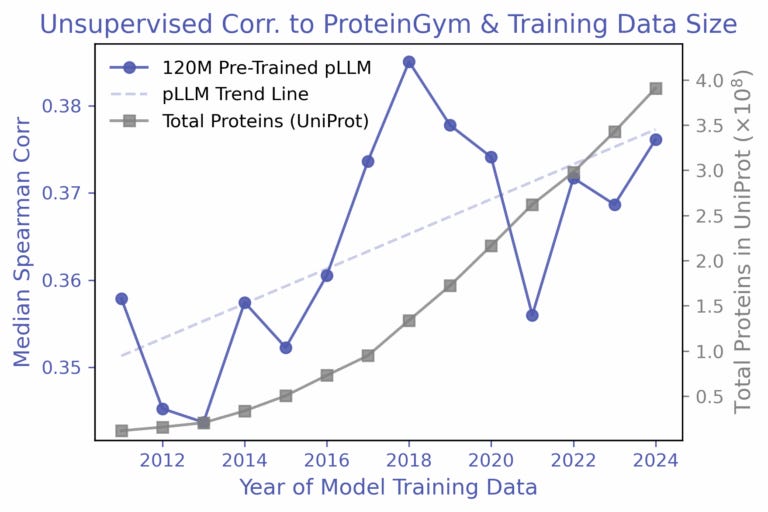
An understanding of scaling laws has allowed natural language processing (NLP) researchers to accurately predict the impact of compute, parameters, and data on model loss. Given the relationship, a desired loss target can be selected and the necessary resources to meet that requirement can be derived. With the stagnation of protein variant effect prediction even with ever growing databases, Align Bio sought to answer whether this same sort of empirical relationship can be applied to protein language models (pLMs).
To investigate this question, the team elected to train the AMPLIFY suite of pLMs with a zero-shot approach on yearly snapshots of UniRef100 from 2011 to 2024, holding all else constant. From their results, they found that the increase in performance, as measured by the Spearman correlation, fluctuated quite significantly, and even decreased some years with the addition of billions of new protein sequences. A follow-up experiment which employed a simple linear regression approach with AMPLIFY embeddings did show consistent improvement as more labeled data was added, but a further trial with a targeted β-lactamase dataset exhibited no improvement over the years, implying that the relationship with labeled data is rather nuanced.
From their observations, the authors conclude that the size of the dataset is not the predominant driver of predictive capability, but rather the diversity within the training set is. The later years were often dominated by redundant sequences, and relative composition of the dataset was also in constant flux with events like the COVID-19 pandemic increasing the relative percentage of a specific group of proteins. To address the issues facing reliable scaling laws in biology, the authors emphasize the need for proper data hygiene and dataset diversity, while also highlighting concerns regarding the scarcity of labels and the generalizability of models.
Papers
Accurate somatic small variant discovery for multiple sequencing technologies with DeepSomatic [Park and Cook et al., Nature Biotechnology, October 2025]
Special thanks to the team at Google for reaching out with the paper pre-release!
...Why it matters: Accurately classifying the thousands of somatic variants that contribute to cancer is a challenging task in precision oncology research. While the vast
This excerpt is provided for preview purposes. Full article content is available on the original publication.